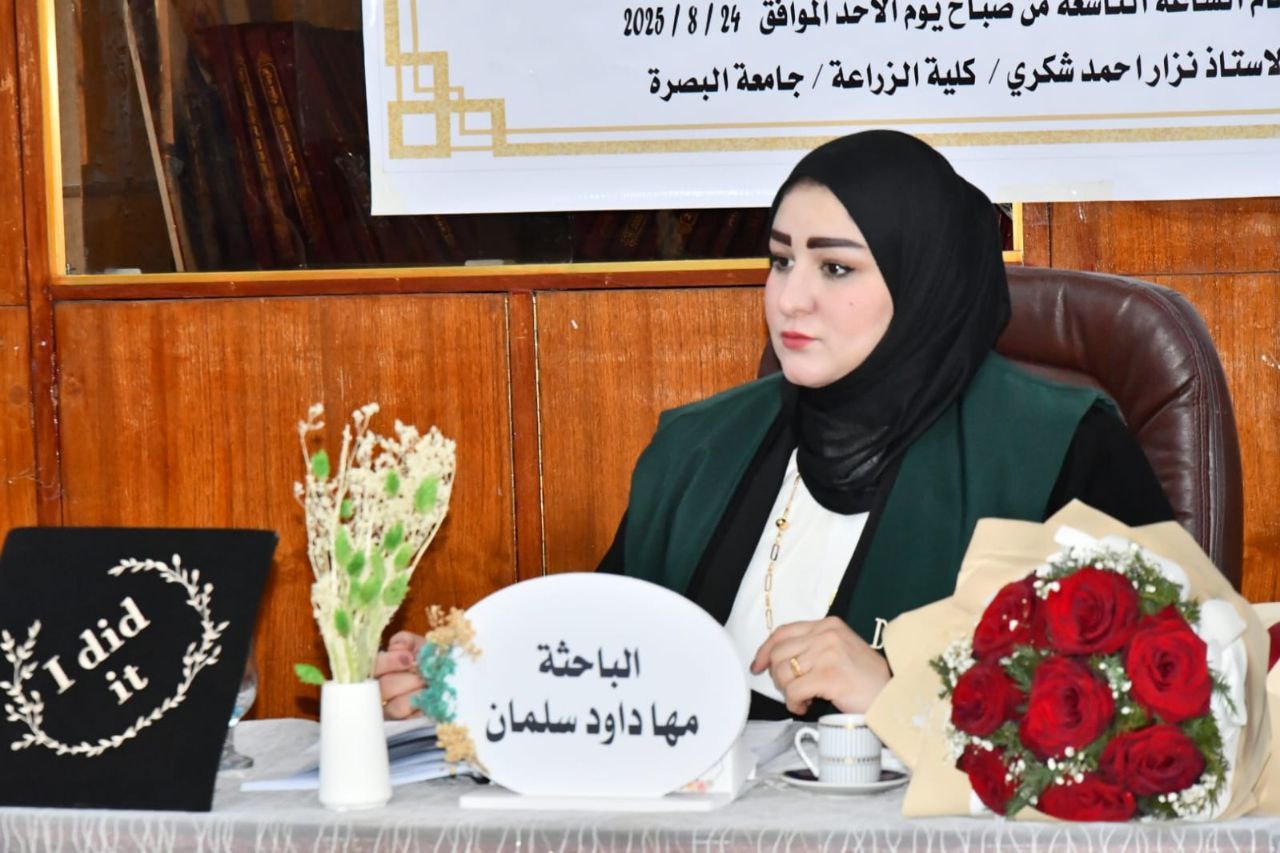
A master's thesis at the College of Agriculture at the University of Basra examined the identification of active compounds and enzymes in local queen bee food and its antioxidant potential.
The thesis, presented by researcher Maha Dawood Salman, aimed to identify the active compounds and enzymes in local queen bee food and study its antioxidant potential.
The study included collecting royal jelly samples from Basra, Baghdad, and Sulaymaniyah. The presence of 10-HAD was identified and its concentration was determined to determine the quality of the royal jelly. The chemical content, mineral elements, and pH values were estimated. The active compounds in the royal jelly were qualitatively and quantitatively assessed. The basic sugars were identified using HPLC-IR, and its enzymatic activity was tested using diastase and invertase enzyme activity tests. Its fatty acid content was studied using GC-MS. FTIR spectroscopy was performed to reveal the composition of the royal jelly. The bioactive peptide was identified using HPLC, then separated and purified using an ÄKTA Pur-25. Its amino acid content was analyzed, and the antioxidant potential of the royal jelly was assessed.
Department of Media and Government Communication / College of Agriculture